health
9 early warning signs of heart disease
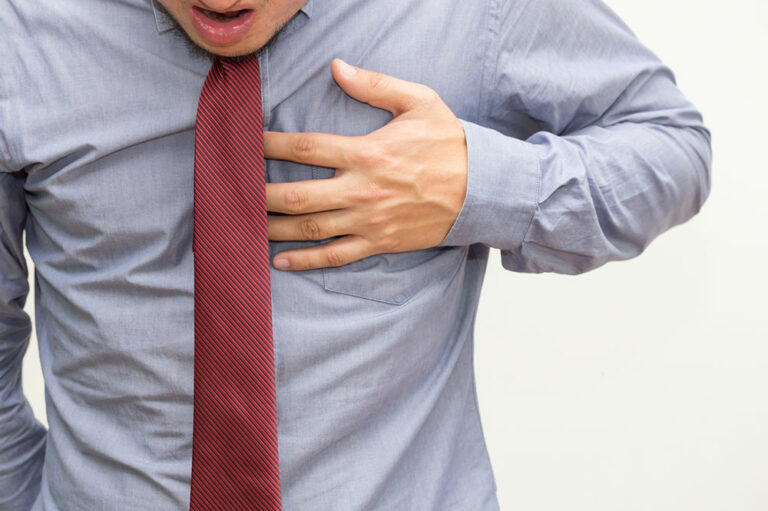
Heart diseases encompass a range of cardiovascular disorders that affect the functions of the heart. Some common heart diseases include blood vessel disease, heart valve disease, arrhythmias, or even heart failure or heart attack. In many cases, the early symptoms of heart disease may not be obvious, like sharp chest pain. Thus, it’s essential to make note of some early signs, as mentioned below, and seek immediate professional help to rule out potential heart issues. Minor chest discomfort This can feel like a tightness in the chest, minor throbbing pain, or pressure in that area. Oftentimes, it may be a result of having bad food, indigestion, or acid reflux, but if there are no lifestyle changes and one still experiences persistent chest discomfort, it’s best to get it checked. Also known as angina, this symptom is more common in heart valve disease and coronary artery disease, where plaque or cholesterol deposits cause blockages in major blood vessels. Heartburn or nausea At times, heart issues can cause gastrointestinal problems like heartburn or nausea, especially for women. Pain in the arms Those suffering a tingling pain that travels down the left side of one’s arm need to get immediate professional help since it can indicate a heart attack. Persistent cough Those who seem to have persistent and dry coughs that don’t go away with natural remedies or even some basic attention from the doctor may be experiencing early signs of heart disease. Lightheadedness Another early sign of heart issues is lightheadedness or dizziness, a clear sign of blood pressure. This symptom may crop up or worsen if one stands up too quickly and may also lead to fainting. Loud snoring This can be mistaken for sleep apnea, especially if the snoring is loud or leads to choking, but if this symptom gets prolonged, it may be a result of cardiovascular disease and can put pressure on the heart.